Underfloor underfloor underfloor heating: types, features of choice, laying rules
Proper arrangement of a warm floor involves the most efficient use of thermal energy. To increase the efficiency of the heating system, various heat-saving techniques are used.
One of the main aspects is the insulating substrate under the warm water floor, redirecting heat fluxes from the water circuit to the finish coating. We will examine in detail the features of each type of thermal insulation damper, the intricacies of the choice and installation of bedding material.
The content of the article:
The value of the thermal insulation substrate
Insulating material - an intermediate layer between the subfloor and the water pipe with a coolant. The main purpose of the substrate is to save and redirect heat flows upward, that is, to the living area of the room.
In addition to the task of preserving heat, the intermediate layer performs a number of no less significant functions:
- Waterproofing. In emergency situations, the waterproof substrate will retain water, protect the lower layers of the underground “cake” and prevent water from leaking to the basement. In addition, it eliminates the entry of moisture vapor from the screed to the finish floor.
- Thermal insulation. The interlayer acts as a kind of barrier between elements with different temperatures. Otherwise, contact with a cold floor will contribute to condensation and reduce the characteristic qualities of the insulation.
- Uniform heat distribution. The substrate minimizes the likelihood of obvious temperature differences - there are no excessively warm or cold zones. This feature reduces the negative thermal effect on the finish flooring, appliances and furniture.
- Sound barrier. Most lining materials absorb the sound effect of walking on the floor and improve the overall soundproofing of the room.
The substrate softens shock loads on the base, distributing pressure pointwise - this helps to maintain the integrity of the screed.
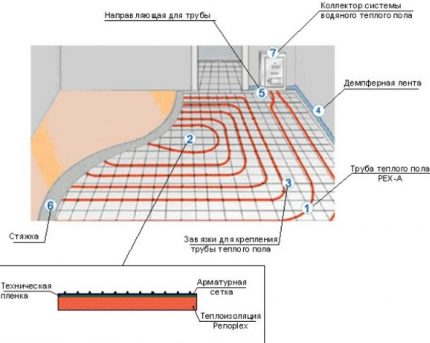
At arrangement of water floor, the substrate is usually laid on a heater for maximum heat storage - the “thermos effect” is realized, which reduces heat loss.

Litter Material Requirements
The characteristics of the substrate are selected depending on the type of roughing substrate, topcoat and operational features of the water floor. However, there is a basic list of properties that any type of bedding material must comply with.
Strength and resilience. As a rule, the heating circuit is embedded in a cement-sand screed. A considerable load on the substrate themselves water system pipes, especially made of metal.

Low thermal conductivity. Optimally, if the heat capacity of the material is combined with its insignificant thickness. The water floor system reduces the height of the room, depending on the type of substrate, the size of the “pie” can be 5-15 cm.
A positive effect gives the ability of the substrate to heat reflection, which ensures the presence of a foil film with reflex properties.
High waterproofing properties. An important characteristic is the percentage of maximum water absorption. The material should not absorb and let moisture pass through it.

Resistance to temperature differences. The declared properties of the substrate should be maintained at different temperature conditions. When choosing, it is important to evaluate such an indicator as permissible operating temperatures. The value of the boundary value is not less than + 70 ° С.
In addition to the indicated requirements, the substrate should not emit toxic, harmful substances. The undoubted plus is the low price, ease of installation.

Types of substrates: assessment of properties and characteristics
Various thermal insulation materials to one degree or another comply with the listed requirements. More than others, slab polystyrene is closer to the ideal. However, in some situations, it is reasonable to use alternative options: foil foamed polyethylene foam, cork backing or moisture-resistant chipboard.
Expanded polystyrene boards - one-stop solution
Expanded polystyrene is the result of industrial foaming of polystyrene. The finished product contains 2% of the main component with auxiliary additives and 98% of gas. The air is enclosed in hermetically sealed cells, which allows the material to maintain good temperature.
The thermal conductivity of expanded polystyrene 10 cm thick is equivalent to a layer of wood of 0.35 m, of reinforced concrete and brick walls - 4.8 m and 1.5 m, respectively.

Technical and operational characteristics of expanded polystyrene:
- Thermal conductivity is 0.028-0.034 W / m * K. The value of the indicator is directly proportional to the density of the insulation.
- Water permeability varies between 0.019-0.015 mg / m * h * Pa. Extruded material is molded by extruding a polymer melt through a slit nozzle.
- Moisture absorption dense polystyrene foam is 0.4%, which is 10 times less in comparison with conventional polystyrene foam. The thermal conductivity of the substrate is maintained even with constant exposure to moisture.
Strength extruded polystyrene compression at linear strain of 10% is 0.25-0.50 MPa, depending on the grade of material.

Weaknesses of polystyrene foam: relatively low soundproofing ability and combustibility. The substrate is afraid of solvents, acetone, turpentine and kerosene - under their influence, the material is deformed.
For thermal insulation, do not choose unpressed or autoclaved polystyrene foam. These species are more fragile.
Extruded or pressed foam mats are suitable as a substrate for a water floor heating - their thermal conductivity is approximately equal. It is popular with consumers. thermal insulation Penopleks.
Cork material - environmental friendliness
The cork lining is made from crushed, pressed wood bark granules using various binders. The main argument in favor of such a substrate is naturalness and absolute environmental friendliness. The material is hypoallergenic and harmless to health.
Additional benefits of cork:
- resistance to deformation - after short-term shock loads it returns to its original form;
- porosity provides high sound absorption properties;
- good thermal insulation characteristics;
- convenience of cutting, styling.
Cork damper is implemented in the form of rolls and individual sheet panels. Products differ in the thickness of the pad: rolled material - 2-4 mm, cork mats - 4-10 mm.

Disadvantages of cork backing:
- vulnerability to moisture;
- exactingness to a waterproofing of a rough floor;
- sensitivity to high static loads.
The classic version of the cork substrate is better not to use under the water floor system. For these purposes, a rubber-cork coating is suitable, where rubber acts as a binder. In addition to water resistance, the damper has improved characteristics of sound and vibration isolation, but it can no longer be called completely natural.

Features of foam polypropylene damper
The simplest and most affordable solution is a polyethylene foam backing. The material is produced by extrusion of polyethylene granules, followed by heat treatment and pressing. The result is an elastic web filled with many air pores.
Depending on the structural features, polyethylene foam substrates are classified into two groups: non-cross-linked and cross-linked.
Non-cross-linked polyethylene foam consists of gas-filled cells up to 3 mm in size. The thickness of the substrate varies from 0.8 to 6 mm, the width of the roll is 1-1.5 m.
The main advantages of such a substrate include:
- high moisture resistance - water absorption of not more than 1%;
- small thickness;
- low cost.
However, non-cross-linked polyethylene foam has more drawbacks.The material is short-lived, quickly wears out, pushes under the weight and, over time, loses its flexibility. The thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.55 W / (m ° C), which indicates insufficient heat conservation.

Crosslinked Polyethylene Foam has the following features:
- phenomenal strength;
- increased density - 33 kg / cubic meter, a similar indicator of cross-linked polyethylene - 25 kg / cubic meter;
- high level of noise absorption - up to 18 dB;
- low level of thermal conductivity - 0.031 W / (m ° C);
- output format in rolls and mats, the thickness of the finished product - 1-20 mm.
The life of the substrate reaches 15 years.

Heat-reflecting metallized substrates
Foil substrates are widely used. Moreover, a different material can be used as a base: extruded polystyrene plate, its non-extruded sibling foam, cork material or polyethylene foam.
In each case, a metallized film improves the initial technical characteristics of the base and complements it with reflex qualities.
The reflective outer coating is made of aluminum and lavsan. The thickness of the foil layer determines the degree of heat reflection of the insulation.

Lavsan is resistant to aggressive environments - the material retains the reflective ability and functions of the hydraulic barrier during prolonged contact with a concrete screed.
Worthy representatives of the heat-reflecting substrate based on polyethylene foam: Penofol, Isoflex, Ecofol. Foamed insulation based on polystyrene foam - Sunpol.
OSB and chipboard - “dry” laying technology
Chipboard materials play the role of a substrate when arranging a warm floor using Finnish technology. The method allows to abandon a monolithic concrete screed.

The floor on a wooden base has a number of features:
- ease of assembly;
- high strength characteristics;
- environmental Safety;
- universality - suitable for decoration with various flooring.
The weak side of the particle board is moisture susceptibility. To increase the hydro and thermal insulation indicators between the pipes and the wooden base, it is recommended to lay a thin substrate, the best option is foil polyethylene.
Substrate selection by type of substrate
Physical features of decorative flooring significantly affect the choice of linear parameters and physical qualities of the substrate. The greater the weight of the finish, the stronger and more reliable the damper should be.
Ceramic tile. Water tiled floor it is equipped with concrete technology - the circuit is mounted under a monolithic screed. This method is associated with significant loads on the lining material.

Laminate. The main criterion for choosing a substrate for a warm water floor with a laminate coating is the highest possible heat saving rate, since the panels themselves do not allow heat to pass through well.
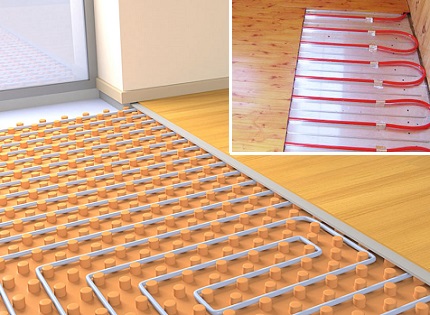
The optimal solution is heat-reflecting insulation with a low degree of thermal conductivity.
Linoleum. Installation of the roll coating is carried out on gypsum board, OSB or sheet plywood. The panels have an impressive weight, which means that the requirements for the strength of the substrate are tightened. It is recommended to give preference to polystyrene, cork options or a backing made of cross-linked polyethylene foam.
Read more about the device for a water heated floor under linoleum written in this article.
Laying technology: a set of basic rules
Mounting the substrate does not present any difficulty, the work can be done independently. The main thing is to follow simple and clear rules.

General requirements for mounting the substrate:
- Accurate calculation. It is necessary in advance to determine the amount of material, taking into account the standard sizes of the pad. Optimally, if the insulation is placed with a minimum number of joints.
- Subfloor preparation. The base should be flat. You should not particularly rely on the ability of a dense material to mask irregularities - any product will eventually take the form of a base.
- Waterproofing. The linings of natural components (cork substrate, chipboard, OSB) require prior installation of the hydrobarrier. Enough to lay dense polyethylene.
- Stacking. Rolled, sheet material is rolled without tension, obligatory overlap on the walls. Plates are placed close to vertical surfaces protected by 10 cm damper tape.
- Docking. Cloths of rolled insulation are overlapped and fixed among themselves with construction tape. Plates and mats are grouped end-to-end.
When arranging a warm floor under a laminate, it is necessary to take into account the orientation of the panels - they are placed mutually perpendicularly with the roll substrate.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
When choosing a substrate, it is better to give preference to products of famous brands. Among the popular brands, both domestic and foreign companies have proven themselves well.
The device of a warm floor using extruded polystyrene "Penoplex":
Placement of the Izolon-500 foam backing under a floating warm floor:
General recommendations for choosing a heater for laying the water circuit:
The value of the insulating substrate under the underfloor heating is difficult to overestimate. The efficiency and profitability of the heating system largely depend on its quality, as well as its compliance with the flooring and the technology of placing the "water coil".
Looking for a substrate for a water heated floor? Or is there experience installing and using a certain type of heat-insulating litter? Please leave comments on the article, ask questions and participate in discussions. The contact form is located below.

 Insulation for warm water floors: rules for selection and installation
Insulation for warm water floors: rules for selection and installation  Warm water floor in a private house: diagrams, device rules + installation instruction
Warm water floor in a private house: diagrams, device rules + installation instruction  How to make a warm floor under the tile: laying rules + installation guide
How to make a warm floor under the tile: laying rules + installation guide  Infrared carbon warm floor: operating principle and laying rules
Infrared carbon warm floor: operating principle and laying rules  How to make a water heated floor under linoleum: design rules and an overview of installation technology
How to make a water heated floor under linoleum: design rules and an overview of installation technology  Infrared film for underfloor heating: types of films, how it works, laying rules
Infrared film for underfloor heating: types of films, how it works, laying rules  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
I took extruded polystyrene foam with the marking 35 on the device of my underfloor heating. There is compressive strength with a large margin. The higher the class, the more expensive, but what is the point of throwing out extra money?
As for the flammability and its other “drawbacks” mentioned here, this is not about the warm floor, because this whole cake is in the screed, and there it is not threatened by fire or solvents.
Many generally cost non-cross-linked polyethylene foam, which has a high moisture resistance and low cost. The combination of these two qualities makes this material a running material for use as a substrate for a water floor heating. But it’s better to add some money and take cross-linked polyethylene foam, which has a higher strength indicator.
In your case, the use of extruded polystyrene foam with marking 35 as a substrate is a very practical solution. You don’t have to worry about the flammability of the material, there’s simply nothing to burn under the screed due to the lack of oxygen. But this material has a relatively low noise insulation index relative to crosslinked polyethylene foam. So keep that in mind.